Unstained samples
Unstained samples
Some specimens composed of elements with higher atomic numbers are inherently electron-dense and can be imaged without applying any staining. Many crystalline powders or engineered nanoparticles for instance can simply be applied to lacey or holey carbon film grids and can immediately be imaged in bright-field TEM or STEM mode, or their elemental composition and crystallinity can be analysed by EDX and SAED.
Calcium phosphate wet precipitate before (left) and after (right) autoclave treatment (Karin Müller, CAIC, doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.10.041).
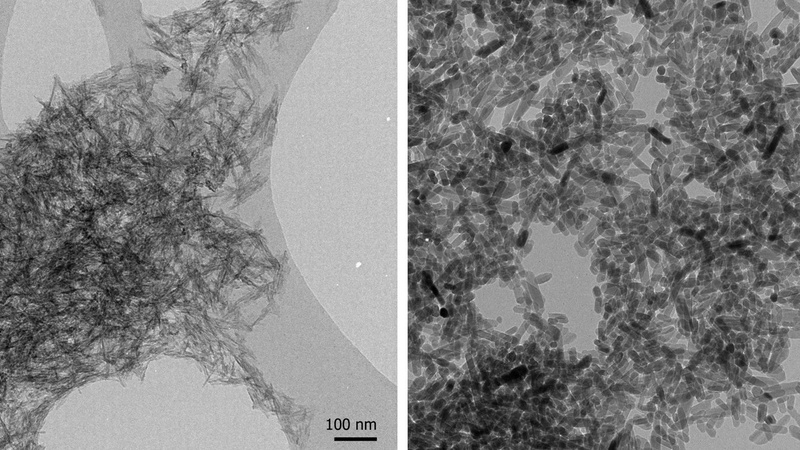
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes with remnants of iron catalyst (Karin Müller, Prof. Krzysztof Koziol, Prof. Slawek Boncel, then Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology, Cambridge).
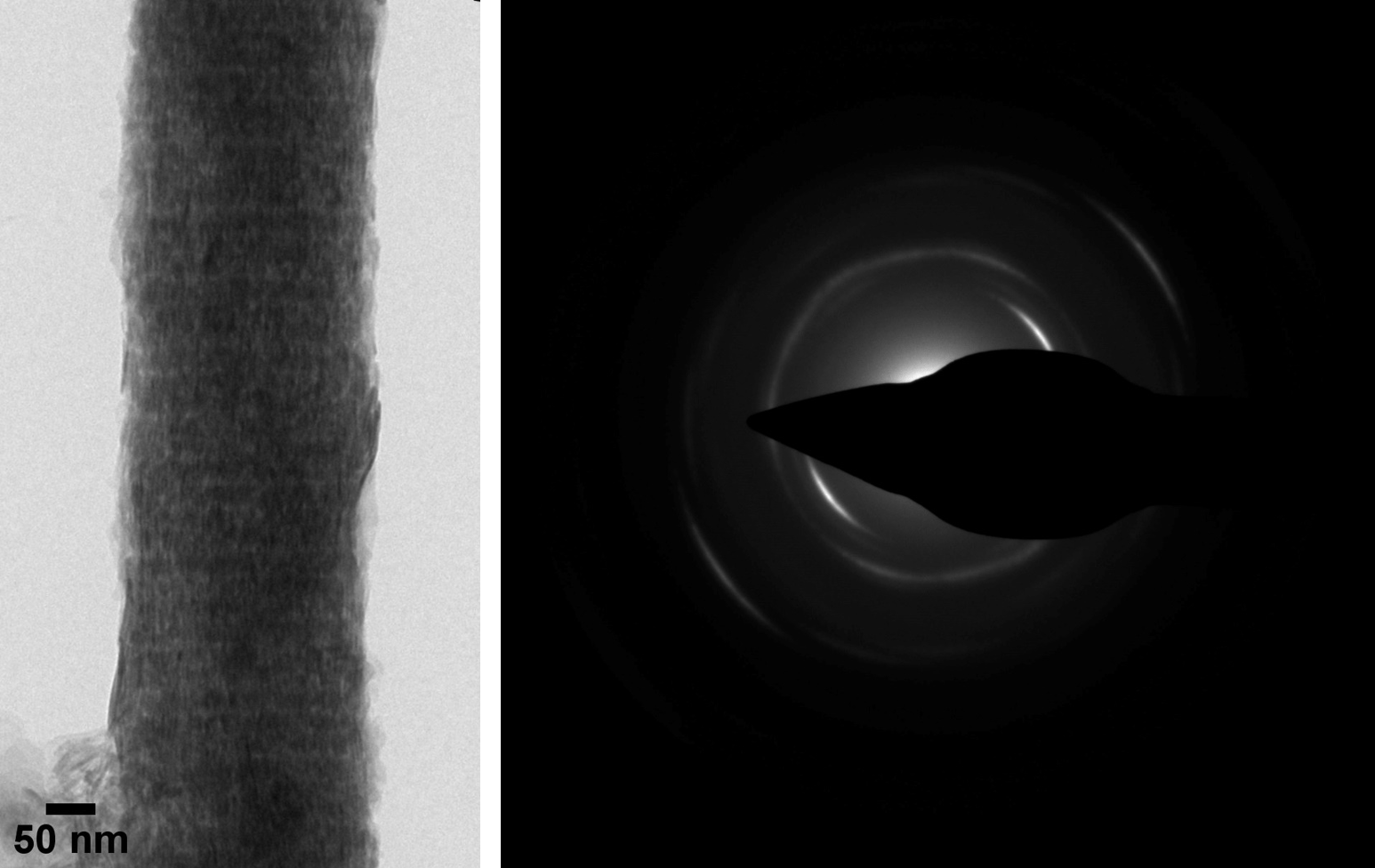
Bovine tendon collagen mineralized in vitro; the arc-shaped SAED pattern indicates the ordered orientation of the calcium phosphate mineral platelets along the fibril (Karin Müller, Prof. Melinda Duer, Prof. Cathy Shanahan; doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.038).
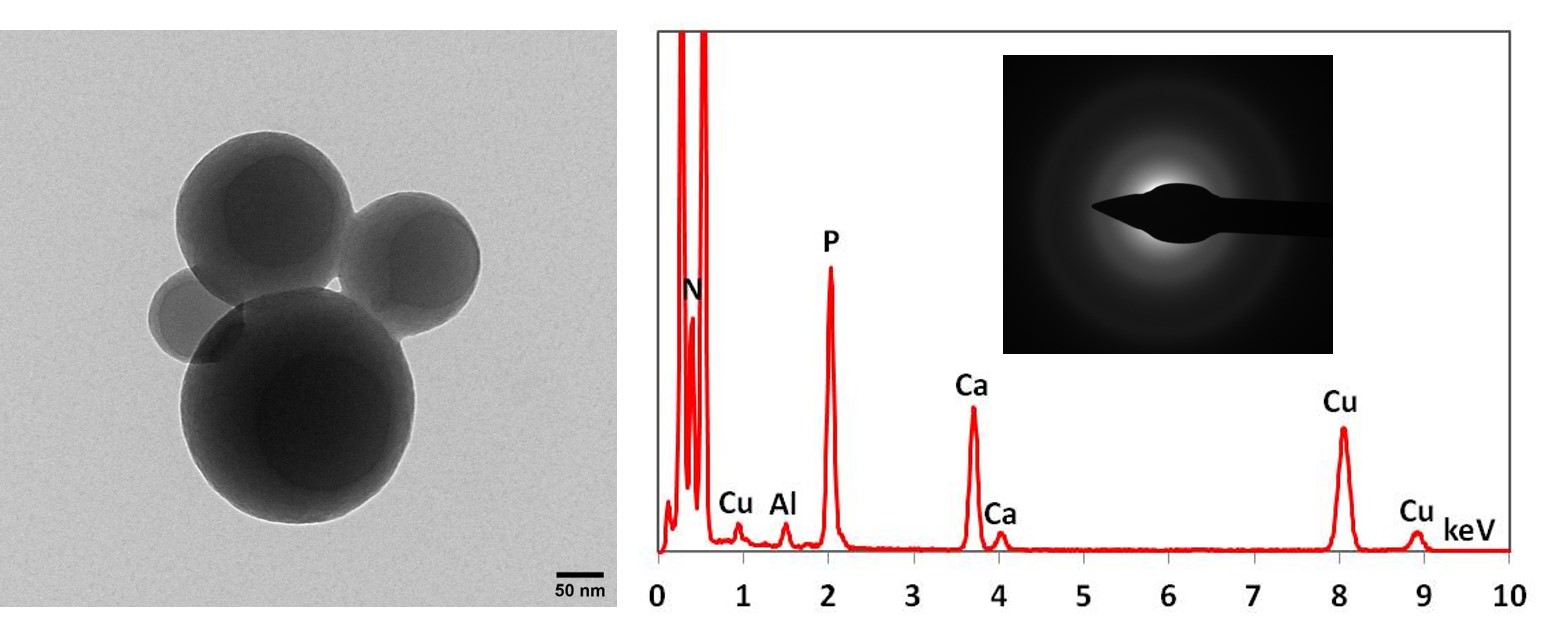
PAR-Ca spheres formed after incubation of the polysaccharide poly (ADP ribose) with calcium ions. The EDX spectrum shows peaks for PAR-bound calcium, the phosphorus peak is derived from the pyrophosphate groups of PAR. The SAED shows the amorphous nature of these spheres (Karin Müller – CAIC; Prof. Melinda Duer – Dept. of Chemistry, Cambridge; Prof. Cathy Shanahan – King’s College London).